How To Create One To One Relationship
Configure One-to-Zero-or-One Relationship in Entity Framework 6
Here, you will learn to configure One-to-Zero-or-One relationships between two entities.
We will implement a one-to-Zero-or-One relationship between the following Student and StudentAddress entities.
public class Student { public int StudentId { get; set; } public string StudentName { get; set; } public virtual StudentAddress Address { get; set; } } public class StudentAddress { public int StudentAddressId { get; set; } public string Address1 { get; set; } public string Address2 { get; set; } public string City { get; set; } public int Zipcode { get; set; } public string State { get; set; } public string Country { get; set; } public virtual Student Student { get; set; } }
Visit the Entity Relationship section to understand how EF manages one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships.
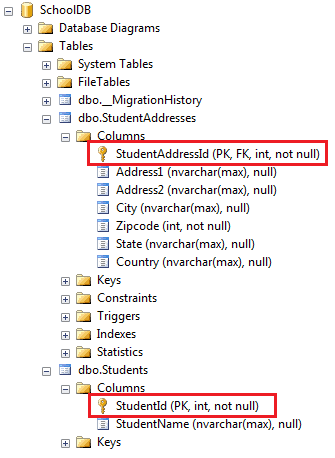
A one-to-zero-or-one relationship happens when a primary key of one table becomes PK & FK in another table in a relational database such as SQL Server. So, we need to configure the above entities in such a way that EF creates the Students and StudentAddresses tables in the DB and makes the StudentId column in Student table as PrimaryKey (PK) and StudentAddressId column in the StudentAddresses table as PK and ForeignKey (FK) both.
Configure One-to-Zero-or-One Relationship using Data Annotation Attributes
Here, we will apply data annotation attributes on the Student and StudentAddress entities to establish a one-to-zero-or-one relationship.
The Student entity follows the default code-first convention as it includes the StudentId property which will be the key property. So, we don't need to apply any attributes on it because EF will make the StudentId column as a PrimaryKey in the Students table in the database.
For the StudentAddress entity, we need to configure the StudentAddressId as PK & FK both. The StudentAddressId property follows the default convention for primary key. So, we don't need to apply any attribute for PK. However, we also need to make it a foreign key which points to StudentId of the Student entity. So, apply [ForeignKey("Student")] on the StudentAddressId property which will make it a foreign key for the Student entity, as shown below.
public class Student { public int StudentId { get; set; } public string StudentName { get; set; } public virtual StudentAddress Address { get; set; } } public class StudentAddress { [ForeignKey("Student")] public int StudentAddressId { get; set; } public string Address1 { get; set; } public string Address2 { get; set; } public string City { get; set; } public int Zipcode { get; set; } public string State { get; set; } public string Country { get; set; } public virtual Student Student { get; set; } }
Thus, you can use data annotation attributes to configure a one-to-zero-or-one relationship between two entities.
Note: Student includes the StudentAddress navigation property and StudentAddress includes the Student navigation property. With the one-to-zero-or-one relationship, a Student can be saved without StudentAddress but the StudentAddress entity cannot be saved without the Student entity. EF will throw an exception if you try to save the StudentAddress entity without the Student entity.
Configure a One-to-Zero-or-One relationship using Fluent API
Here, we will use Fluent API to configure a one-to-zero-or-one relationship between the Student and StudentAddress entities.
The following example sets a one-to-zero or one relationship between Student and StudentAddress using Fluent API.
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { // Configure Student & StudentAddress entity modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .HasOptional(s => s.Address) // Mark Address property optional in Student entity .WithRequired(ad => ad.Student); // mark Student property as required in StudentAddress entity. Cannot save StudentAddress without Student }
In the above example, we start with the Student entity. The HasOptional() method configures the Address navigation property in Student entity as optional (not required when saving the Student entity). Then, the WithRequired() method makes the Student navigation property of StudentAddress as required (required when saving the StudentAddress entity; it will throw an exception when the StudentAddress entity is saved without the Student navigation property). This will also make the StudentAddressId as ForeignKey.
Thus, you can configure a one-to-Zero-or-one relationship between two entities where the Student entity can be saved without attaching the StudentAddress object to it but the StudentAddress entity cannot be saved without attaching an object of the Student entity. This makes one end required.
EF API will create the following tables in the database.
Configure a One-to-One relationship using Fluent API
We can configure a one-to-One relationship between entities using Fluent API where both ends are required, meaning that the Student entity object must include the StudentAddress entity object and the StudentAddress entity must include the Student entity object in order to save it.
Note:One-to-one relationships are technically not possible in MS SQL Server. These will always be one-to-zero-or-one relationships. EF forms One-to-One relationships on entities not in the DB.
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { // Configure StudentId as FK for StudentAddress modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .HasRequired(s => s.Address) .WithRequiredPrincipal(ad => ad.Student); }
In the above example, modelBuilder.Entity<Student>().HasRequired(s => s.Address) makes the Address property of StudentAddress as required and .WithRequiredPrincipal(ad => ad.Student) makes the Student property of the StudentAddress entity as required. Thus it configures both ends as required. So now, when you try to save the Student entity without the StudentAddress entity without the Student, it will throw an exception.
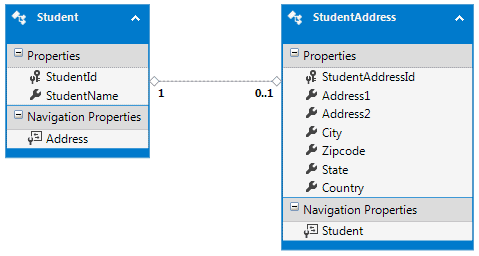
Create a read-only Entity Data Model for the above example using EF Power Tools. The entities will appear like the diagram shown below:
Learn how to configure a one-to-many relationship in the next section.
How To Create One To One Relationship
Source: https://www.entityframeworktutorial.net/code-first/configure-one-to-one-relationship-in-code-first.aspx
Posted by: proctorgoicerouth.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create One To One Relationship"
Post a Comment